Understanding Climate Change
Climate change is extreme variations in weather conditions comprising of increased and decreased temperature (Global Change 2019). Climate change and global warming is the heating of the earth’s atmosphere due to numerous human activities and resulting in countless society, environmental and animal issues.
According to McCabe (2019), climate change is easily described as a coin. He explains that one side of the coin represents surplus carbon and other greenhouse gasses that are released into the atmosphere and the other side of the coin consists of land-use change. This analogy means that both issues of releasing carbon and changing the way we utilise the earth as compared to 100 years ago (mass cattle farms, deforestation, and more), are contributing in forming the same “coin”, which leads to the contribution of increasing rapid climate change.
According to McCabe (2019), climate change is easily described as a coin. He explains that one side of the coin represents surplus carbon and other greenhouse gasses that are released into the atmosphere and the other side of the coin consists of land-use change. This analogy means that both issues of releasing carbon and changing the way we utilise the earth as compared to 100 years ago (mass cattle farms, deforestation, and more), are contributing in forming the same “coin”, which leads to the contribution of increasing rapid climate change.
Earth’s Systems
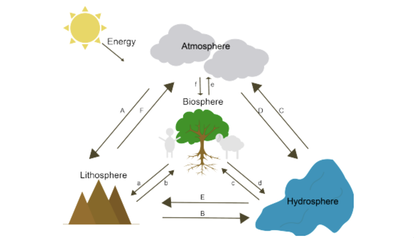
McCabe (2019) explained that “Earth is a closed dynamic system which means if you have burnt toast in your kitchen, you smell it around the house”. This means that energy is passed from the sun to the four earth systems. As shown in the figure below, all these spheres are connected producing a constant moving flow of energy within, so when one sphere is affected with gas discharge, all the other spheres are also effected creating a chain reaction.
The two main elements transferring energy flow between these earth systems are ocean currents and wind. This is important to know because due to excess carbon, caused by climate change, in the ocean (hydrosphere) it alters the speed of the currents resulting in less carbon uptake, because of this there is more carbon in the atmosphere and climate change is aggravated. Wind (atmosphere) patterns also changes and less energy flow takes place, heating the earth’s surface (lithosphere) and so on. It is important for the reader to understand because when one element changes, everything else gets effected, thus it creates a chain reaction.
The two main elements transferring energy flow between these earth systems are ocean currents and wind. This is important to know because due to excess carbon, caused by climate change, in the ocean (hydrosphere) it alters the speed of the currents resulting in less carbon uptake, because of this there is more carbon in the atmosphere and climate change is aggravated. Wind (atmosphere) patterns also changes and less energy flow takes place, heating the earth’s surface (lithosphere) and so on. It is important for the reader to understand because when one element changes, everything else gets effected, thus it creates a chain reaction.
The Carbon Cycle
In the closed dynamic system (figure above), the carbon flows between them. The example of the carbon cycle, in the figure below, is a representation of the process:
Nutrients are released through withering of rocks. These nutrients resolve in water and get absorbed by plants. The animals eat these plants, getting the nutrients. The animals and plants die and the nutrients return to the ground. Nutrients is thus back in the lithosphere and start again. Plants use carbon for photosynthesis. Animals eat these plants and breathe the carbon back into the air. The ocean absorbs the carbon, and the carbon dissolves in the ocean currents. The ocean spray returns the right amount of carbon back into the atmosphere. The cycle continues.
When the carbon cycle is disrupted due to deforestation, burning fossil fuels, overgrazing and other human activities, more carbon is produced and then trapped in the atmosphere creating greenhouse gasses resulting in warmer temperatures.
Nutrients are released through withering of rocks. These nutrients resolve in water and get absorbed by plants. The animals eat these plants, getting the nutrients. The animals and plants die and the nutrients return to the ground. Nutrients is thus back in the lithosphere and start again. Plants use carbon for photosynthesis. Animals eat these plants and breathe the carbon back into the air. The ocean absorbs the carbon, and the carbon dissolves in the ocean currents. The ocean spray returns the right amount of carbon back into the atmosphere. The cycle continues.
When the carbon cycle is disrupted due to deforestation, burning fossil fuels, overgrazing and other human activities, more carbon is produced and then trapped in the atmosphere creating greenhouse gasses resulting in warmer temperatures.